scoped_ptr 与 auto_ptr 与 shared_ptr 区别总结
1.auto_ptr 被复制后,将失去原来所致资源的所有权;
2.scoped_ptr永远不能被复制或被赋值!scoped_ptr拥有它所指向的资源的所有权,并永远不会放弃这个所有权;
3.shared_ptr 是可以共享所有权的智能指针。
测试实例如下:
#include "stdafx.h"
//#include "windows.h"
#include <memory>
#include <iostream>
using std::tr1::shared_ptr;
class Foo
{
public:
Foo()
{
std::cout<<"new Foo()"<<std::endl;
i = 0;
}
~Foo()
{
std::cout<<"destroy Foo()"<<std::endl;
}
void print()
{
std::cout<<"Foo::print"<<std::endl;
}
int i;
};
void OutSharePtr(shared_ptr<Foo> &P)
{
Foo* p = new Foo();
shared_ptr<Foo> sp1(p);
std::cout<<sp1.use_count()<<"::"<<sp1.get()<<std::endl;
shared_ptr<Foo> sp2(sp1);
p->print();
sp2->print();
std::cout<<sp1.use_count()<<"::"<<sp1.get()<<std::endl;
P = sp2;
std::cout<<sp1.use_count()<<"::"<<sp1.get()<<std::endl;
}
void InSharePtr(shared_ptr<Foo> &p)
{
p->i += 100;
std::cout<<p.use_count()<<"::"<<p.get()<<std::endl;
}
#include <algorithm>
char upCase(char c)
{
return toupper(c);
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
shared_ptr<Foo> sp1(new Foo());
shared_ptr<Foo> sp2(sp1);
shared_ptr<Foo> sp3;
sp1->print();
sp2->print();
std::cout<<sp1.use_count()<<"::"<<sp1.get()<<std::endl;
std::cout<<sp3.use_count()<<"::"<<sp3.get()<<std::endl;
sp3.swap(sp1);
std::cout<<sp1.use_count()<<"::"<<sp1.get()<<std::endl;
std::cout<<sp3.use_count()<<"::"<<sp3.get()<<std::endl;
sp3.reset();
std::cout<<sp1.use_count()<<"::"<<sp1.get()<<std::endl;
sp2.reset();
std::cout<<sp1.use_count()<<"::"<<sp1.get()<<std::endl;
sp1.reset();
std::cout<<sp1.use_count()<<"::"<<sp1.get()<<std::endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果截图: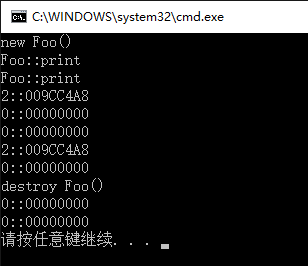
scoped_ptr auto_ptr shared_ptr
上一篇:[精华] VC中BSTR、Char和CString类型的转换
下一篇:boost多索引容器multi_index_container实战

 评论加载中,请稍后...
评论加载中,请稍后...